 Home Page > KernelCAD Models > Mathematical Objects > 2D Elements > Arcs Home Page > KernelCAD Models > Mathematical Objects > 2D Elements > Arcs
Arcs
Two dimensional Arcs
An arc is a 2D line, which is a part of a circumference. Only arcs which
are not longer than half of the full circumference are considered valid in
DInsight software.
An arc is fully determined by two points of its ends and its curvature.
Curvature is a real number, which defines how curved is the segment.
Absolute value of curvature is an inverse of radius of the correspondent circumference:
Curvature = 1/Radius; Radius =
1/Curvature.
In DInsight software straight lines are considered a special case of arc.
Straight lines are considered arcs with zero curvature (and infinite
radius).
In an arc distance between its ends is always less or equal to double
radius, otherwise the arc is considered invalid
and does not have geometrical meaning. Arcs with curvature 0 (straight
lines) are always valid.
When distance between its ends is equal double radius the arc is
called full arc.
Ends of Arcs (and lines) are distinguished as first end the last end.
Curvature and radius in DInsight software can be negative.
Geometrically an arc has positive curvature and radius if the arc is
located on the right hand side while moving from the first end to the last
end along the a straight line.
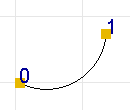
Fig 1. Positive arc.
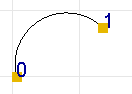
Fig 2. Negative arc.
Normally Arcs are present only as a part of a line strip. In a strip arc
itself and its ends are considered different elements because they can be
selected independently. That is why as a geometric element
arc has a single parameter - curvature or radius.
Primary Properties
Primary properties completely and uniquely define geometry of an arc.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Interface |
|
FirstEnd |
2D Point |
The first end of the arc |
ILine2D
|
| SecondEnd |
2D Point |
The second end of the arc |
ILine2D |
| Curvature |
double |
Curvature (=1/radius) of the
arc |
IArc |
Secondary Properties
Secondary properties like center of the arc are the ones calculated via
IArcEx interface. They uniquely
are defined by primary properties.
Points of an arc are often parameterized with ratio (length or
partial arc between the first end and the point) / (length of the whole
arc). This parameter always belongs to [0, 1] range, where 0 and 1 are
mapped to the first and the second ends.
PProgrammatic access
Primary properties of an arc are accessed via
ILine2D and
IArc interfaces. Additional
calculations related to an arc can be performed with
IArcEx
To create a new arc call IObjectGenerator.Create
method with eType parameter set to eObjTypeArc.
|